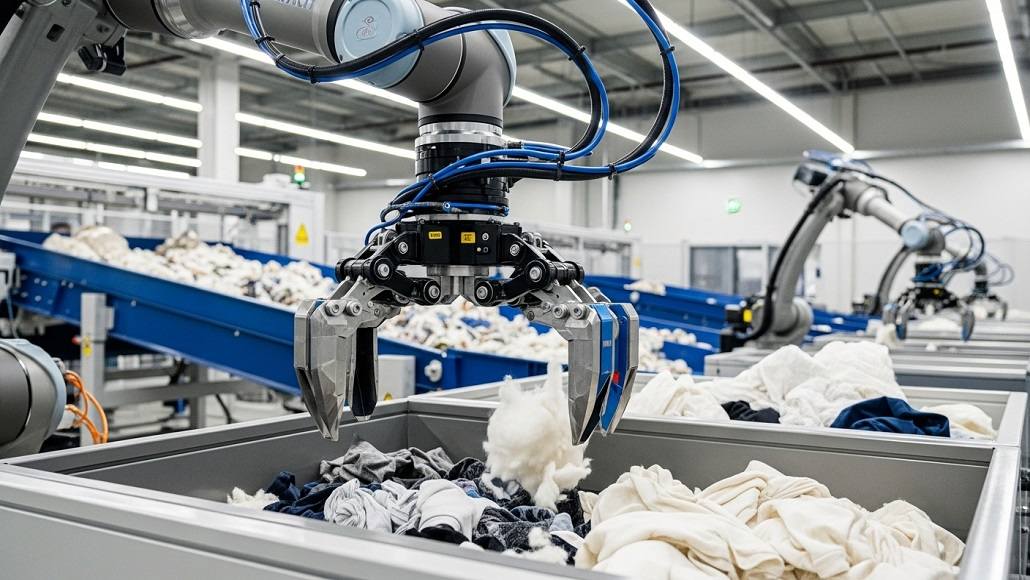
For centuries, textile manufacturing has signified pivotal advancements in industrial history, evolving from the spinning jenny to steam-powered looms and, more recently, to electrification. Now, the industry stands on the cusp of yet another revolutionary transformation: the integration of Industry 4.0 in textile manufacturing. This new wave, characterized by intelligent automation, data connectivity, and machine learning, is fundamentally changing the landscape of textile production.
Smart factories are emerging as the new operational norm across global textile hubs—from Coimbatore to Guangzhou, Istanbul to North Carolina. These facilities are not merely experimental sites; they represent a significant shift in manufacturing practices, reshaping how textiles are produced and marketed.
Defining Industry 4.0 in Textiles
Industry 4.0 in textile manufacturing encapsulates the fourth industrial revolution where machines, data, and advanced analytics converge to form self-optimizing production environments. In the textile sector, this involves interconnected looms, real-time production dashboards, predictive maintenance systems, and fully digital supply chains.
The changes brought about by Industry 4.0 are not superficial; they are foundational. In traditional spinning or weaving mills, oversight relies on human intervention and reactive measures. Conversely, smart factories utilize embedded sensors to transmit continuous performance data to centralized systems. These systems employ AI to predict machine failures, autonomously adjust operational parameters, and even reconfigure production lines based on variable demand.
As the textile industry, often seen as slow to embrace innovation, reaches a critical turning point, firms are increasingly turning to smart manufacturing not just for efficiency but for survival amid rising cost pressures and heightened consumer expectations.
Data-Driven Operations in Real-Time
At the heart of every advanced textile factory lies data. Each piece of equipment, from looms to dyeing machines, is linked within an industrial internet of things (IIoT) network, collecting vital metrics such as spindle speed, tension, energy consumption, and output quality.
The true value of this data emerges from its application. For instance, a leading knitwear manufacturer in Tiruppur, India, recently introduced a cloud-based monitoring system that enhanced machine utilization by 14% and reduced fabric rejections by 9% within six months. This was largely achieved through early detection of issues, allowing for timely interventions.
In Turkey, a denim producer serving European and North American markets employs AI to optimize finishing processes. By integrating sensory data from their washing machines with an AI model, the system dynamically adjusts water flow, enzyme dosage, and cycle times, leading to 22% reductions in water use and an 18% faster turnaround.
Smart Automation: Beyond Speed
While automation has long been present in the textile industry, what sets Industry 4.0 in textile manufacturing apart is the layer of intelligence it introduces. In Germany, for instance, a dye house has transformed the labor-intensive color matching process through the use of spectrophotometers and AI-driven tools that generate precise dye formulas, thus minimizing human error and speeding up production.
Processes like spinning and carding are increasingly managed by adaptive algorithms that autonomously adjust operational metrics based on real-time environmental conditions, enhancing efficiency without human oversight. Importantly, this smart automation does not eliminate jobs; rather, it redefines them. Factory workers are now trained to manage digital interfaces and monitor performance, shifting their focus from manual tasks to overseeing automated processes.
Predictive Maintenance and Machine Well-Being
Predictive maintenance has been one of the earliest successes in the realm of smart textile factories. Traditionally, unexpected machine breakdowns resulted in costly downtimes and quality issues. Industry 4.0 introduces condition-based maintenance strategies. By analyzing data such as vibrations and temperature fluctuations, systems can predict equipment failures and schedule maintenance precisely, cutting down on unplanned stoppages and repair costs.
For example, a dyeing plant in Vietnam that adopted this predictive model reported a 38% decrease in unexpected machine failures in its first year of operation, attributing this improvement to sensor-based monitoring and AI-driven maintenance planning.
Integration Across the Value Chain
One of the most transformative elements of Industry 4.0 in textiles is its capacity to unify various functions within the value chain. Modern textile enterprises are becoming more digitally interconnected, linking ERP systems, CAD software, and logistics systems seamlessly.
For apparel exporters, this results in expedited lead times and enhanced order tracking. Home textile manufacturers benefit from producing smaller, customized runs, while technical textile producers gain real-time compliance tracking and traceability.
In Bangladesh, a vertically integrated manufacturer has connected its dyeing, cutting, sewing, and packing operations through a unified digital platform. Managers in Dhaka and buyers in London can access real-time dashboards that display order status, shipment readiness, and inventory levels, resulting in a 28% reduction in average order processing time and a 94% on-time delivery rate.
The initial investment was substantial, but the return on this digital transition was realized within just 18 months.
Barriers and Future Pathways
Despite the growing momentum, the widespread adoption of Industry 4.0 in textiles remains inconsistent. Challenges include high initial capital requirements, a scarcity of skilled digital talent, legacy machinery compatibility issues, and resistance to change within organizations.
Small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which dominate the textile landscape in emerging economies, often find it daunting to transition fully. Many choose to implement only partial digital solutions, such as isolated ERP systems or individual machine monitoring, rather than developing a cohesive digital strategy.
However, government initiatives and industry collaborations are emerging to facilitate this transition. In Italy, for instance, the “Piano Transizione 4.0” tax incentive program has spurred numerous textile SMEs in regions like Prato and Biella to upgrade their machinery and digitize operations. Similar incentives are being introduced in countries such as India, Vietnam, and Egypt.
The trend is clear: early adopters of Industry 4.0 in textile manufacturing are gaining competitive advantages, while late entrants may struggle to keep pace in terms of efficiency, transparency, and speed.
Conclusion
The textile industry has always been a landscape of evolution, but Industry 4.0 represents a monumental shift in operational practices. Rather than merely enhancing existing processes, it redefines how factories respond to market demands and measure their success.
Smart factories today are characterized not just by automation but by adaptability, connectivity, and intelligence. As global consumers increasingly demand speed, transparency, and accountability, the digital infrastructure of manufacturing becomes a crucial competitive advantage.
Textile manufacturers embracing Industry 4.0 are not merely modernizing their operations; they are ensuring their relevance in an ever-evolving global market. In the fabric of tomorrow’s industry, intelligence is the vital thread that will hold it all together.