Key Takeaways
- Climate-responsive textiles automatically adjust breathability, insulation, and moisture management in response to temperature changes
- Phase-change materials absorb excess body heat when wearer temperature rises, releasing stored heat when ambient temperature drops
- Dual-mode fabrics provide independent control of thermal management and moisture transport enabling optimal comfort across varied conditions
- Responsive textiles utilizing nano-coatings adapt surface properties enabling active heat dissipation during warm conditions while maintaining insulation during cool periods
- Lightweight thermal structures provide superior warming without bulk, eliminating requirement for heavy outerwear across extended seasons
- Breathability optimization enables active perspiration management preventing both overheating and excessive moisture accumulation
- Sustainable climate-responsive textiles reduce seasonal wardrobe rotation requirement, decreasing total consumption and environmental impact
The Science of Adaptive Thermal Management
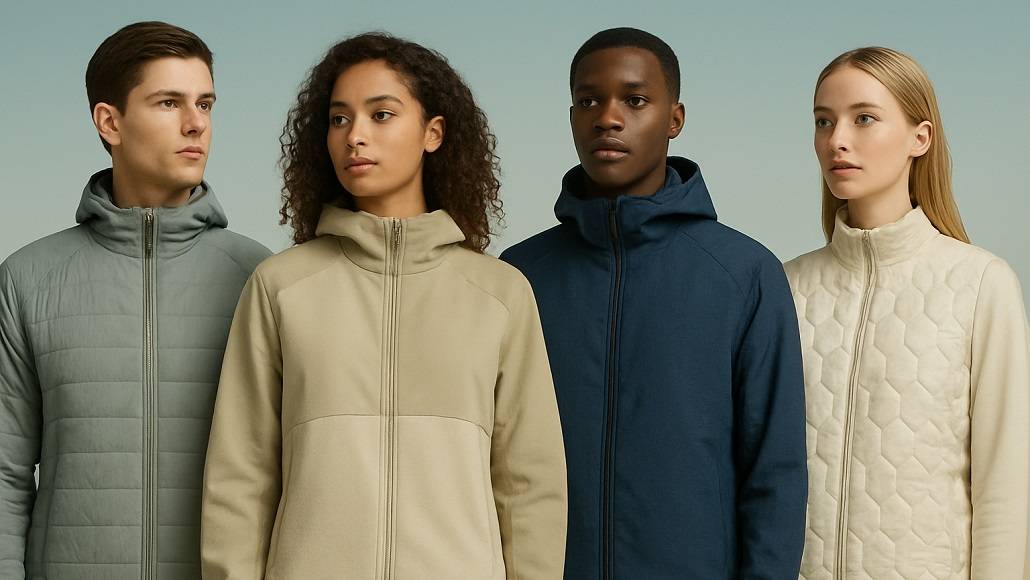
Climate-responsive fashion represents convergence of textile engineering and environmental science, creating fabrics that actively manage thermal comfort across varying conditions. Rather than requiring wearer adjustment through layering or clothing changes, responsive textiles modify their properties in response to body temperature and environmental conditions. This active adaptation represents remarkable technological achievement providing unprecedented comfort while reducing wardrobe requirements and seasonal consumption patterns.
The mechanisms underlying climate-responsive textiles involve sophisticated material science integrating multiple technologies. Phase-change materials (PCMs) embedded within fabrics represent perhaps the most significant innovation—these specialized compounds absorb excess body heat when wearer temperature rises above specific thresholds, then release stored heat when ambient temperature drops below activation points. This dynamic regulation maintains consistent comfort without wearer intervention.
Contemporary climate-responsive textiles increasingly incorporate multiple simultaneous functions rather than addressing single characteristics. Fabrics managing both thermal regulation and moisture transport simultaneously enable optimal performance across diverse conditions. This multifunctional approach reflects actual environmental complexity where temperature alone does not determine wearer comfort—moisture accumulation, air movement, and radiation also influence thermal sensation significantly.
Thermoregulatory Fiber Development
Advanced thermoregulatory fibers engineered specifically for climate response represent frontier of performance textile innovation. These fibers incorporate PCM microcapsules, conductive coatings, or responsive polymer structures enabling active thermal management at material level. The integration of thermal regulation into fiber structure itself rather than applying treatment to finished fabric provides superior performance and durability—functional properties persist across extended wear and multiple washing cycles.
Thermoregulatory fiber development addresses key fashion trend toward multifunctional apparel. Contemporary consumers increasingly expect single garments to function across extended temperature ranges rather than requiring complete wardrobe changes with seasons. Thermoregulatory fibers enable this expectation through intelligent material composition automatically adapting to environmental conditions.
The commercialization of thermoregulatory fibers has accelerated substantially as performance validation demonstrates genuine consumer benefits. Athletes utilizing thermoregulatory activewear report measurable performance improvements through maintained optimal temperature. Professional workers in temperature-variable environments appreciate extended comfort and reduced requirement for constant wardrobe adjustment. These real-world applications drive continued investment in thermoregulatory fiber research and development.
Breathability Innovation and Moisture Management
Breathability represents critical component of climate-responsive textile performance, enabling efficient perspiration evaporation while maintaining insulation against wind and external moisture. Contemporary climate-responsive textiles incorporate sophisticated moisture management systems utilizing fiber hygroscopicity, nano-coatings, and structural design features enabling simultaneous insulation and moisture transport.
Dual-mode moisture management systems enable independent control of vapor transport and liquid water resistance—allowing perspiration evaporation while repelling rain and external moisture. This capability represents remarkable technological achievement, as traditional textiles typically sacrifice one property for another. Contemporary responsive textiles achieve both simultaneously through innovative fabric construction and intelligent material selection.
Lightweight breathable insulation represents emerging trend addressing fashion consumer desire for thermal comfort without bulk and weight. Traditional outerwear required substantial material thickness to provide adequate insulation. Contemporary thermoregulating lightweight structures achieve equivalent performance through superior insulating fibers and intelligent material combination. This advancement enables versatile seasonal garments functioning across temperature ranges previously requiring separate items.
Nano-Coating Technologies and Surface Adaptation
Nano-coating technologies enable creation of intelligent fabric surfaces that adapt properties in response to environmental stimuli. Superhydrophobic nano-coatings provide water-repelling properties without compromising breathability. Photocatalytic coatings utilize sunlight to trigger enhanced cooling effects maintaining wearer comfort during intense solar exposure. Thermochromic coatings change color in response to temperature variation, providing visual feedback regarding thermal properties.
The sophistication of contemporary nano-coating technologies enables multiple simultaneous functions within single fabric surface. Antibacterial properties extend wear duration between laundering. Odor-control finishing manages olfactory comfort. UV-protective coatings prevent sun damage. These multifunctional approaches reflect consumer demand for apparel that performs comprehensively across diverse applications and environmental contexts.
Nano-coating durability has improved substantially, with contemporary treatments maintaining function across dozens of wash cycles. This durability improvement has transformed nano-coating applications from specialized luxury treatment to increasingly accessible performance enhancement. As production scales and manufacturing efficiency improves, nano-coating costs decline, making climate-responsive functionality increasingly mainstream rather than premium positioning.
Seasonal Textile Adaptation and Extended Wear
Climate-responsive fashion enables single garments to function effectively across extended temperature ranges, reducing seasonal wardrobe rotation requirement and associated consumption and waste. Spring garments can function across summer through autumn seasons through intelligent fabric properties automatically adjusting to changing conditions. This extended functionality directly addresses contemporary fashion trends emphasizing sustainability through reduced consumption.
The environmental benefits of extended wear seasons and reduced clothing requirement cannot be overstated. Manufacturing, distribution, and laundering represent substantial proportion of apparel environmental impact. Reducing clothing quantity through extended seasonal functionality decreases total lifecycle environmental impact substantially. This sustainability advantage positions climate-responsive textiles advantageously within broader fashion industry movement toward environmental responsibility.
Consumer adoption of climate-responsive apparel demonstrates willingness to invest in higher-cost items providing sufficient value through extended functionality and environmental alignment. Brands marketing climate-responsive textiles emphasizing sustainability credentials alongside comfort benefits appeal to environmentally conscious consumers increasingly willing to prioritize conscious consumption over quantity accumulation.
Active Temperature Management and Energy Harvesting
Emerging climate-responsive technologies enable active temperature management through energy harvesting integrated into garment structures. Fibers incorporating photovoltaic properties generate electricity from ambient light, powering thermoregulatory systems. Piezoelectric fibers capture mechanical energy from wearer movement, providing power for active cooling or heating elements. These energy-harvesting approaches enable self-powered garments requiring no battery charging.
The integration of energy harvesting with climate-responsive functionality creates closed-loop systems where garments generate power required for their own operation. This technological sophistication appeals to contemporary consumers valuing innovative functionality and sustainability simultaneously. Garments that optimize their own thermal performance through generated energy represent remarkable convergence of technology and sustainability.
Responsive Textiles and Health Monitoring Integration
Contemporary climate-responsive textiles increasingly incorporate biometric monitoring capabilities alongside thermal management functions. Embedded sensors monitor core body temperature, skin temperature, and perspiration rates, enabling garments to adjust thermal properties optimally for individual physiological responses. AI algorithms analyze collected data, providing health insights regarding thermal stress, activity efficiency, and recovery patterns.
The integration of health monitoring with climate-responsive function creates intelligent apparel anticipating wearer needs and optimizing comfort proactively rather than reactively. Garments learning individual thermal preferences through extended wear can customize responses increasingly precisely. This personalized approach appeals to contemporary consumers expecting tailored functionality reflecting individual characteristics and preferences.
The Future of Climate-Responsive Fashion
The trajectory of climate-responsive textile development suggests continued acceleration in technological sophistication and mainstream adoption. As manufacturing scales and costs decline, climate-responsive functionality will likely transition from premium positioning to competitive necessity across apparel segments. Future development will likely emphasize seamless functionality—with responsive properties becoming invisible to wearers while delivering measurable benefits.
The intersection of climate-responsive textiles with sustainable fashion philosophy creates compelling future possibilities. Garments enabling extended functionality across seasons and temperature ranges directly support sustainability objectives through consumption reduction. As climate awareness intensifies and environmental regulation increases, climate-responsive fashion will likely become industry standard rather than innovation frontier. The convergence of performance, sustainability, and consumer preference positions climate-responsive textiles advantageously within coming decade’s fashion evolution.