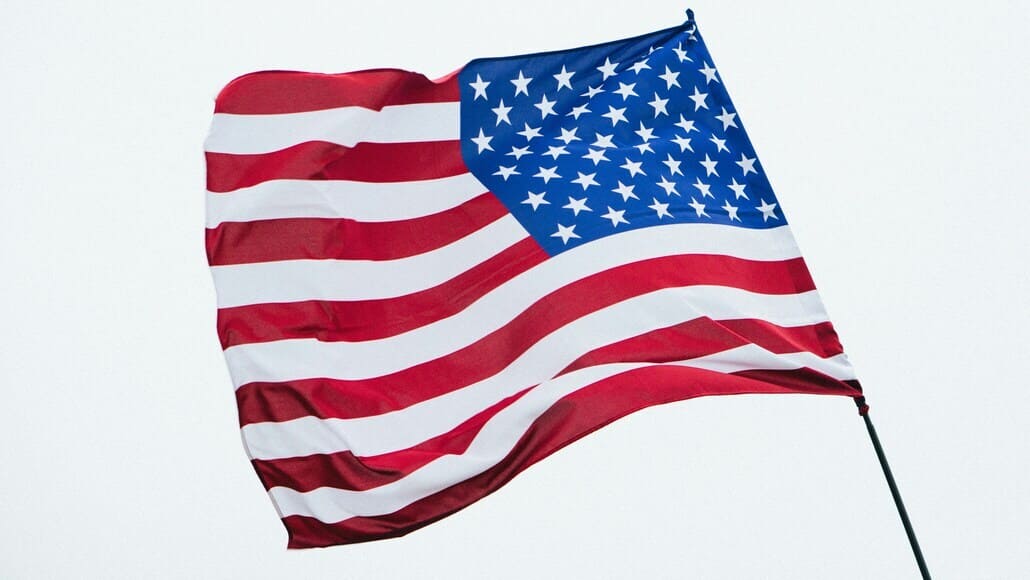
The implementation of tariffs by the Trump administration significantly impacted the global textile industry. These tariffs, primarily targeting Chinese imports, sought to reduce the U.S. trade deficit and protect domestic industries. However, the textile sector experienced mixed consequences as a result.
China, being one of the largest exporters of textiles and apparel, was heavily affected by the tariffs. This prompted many companies to explore alternative sourcing options, such as Vietnam, Bangladesh, and other Southeast Asian countries, to mitigate the additional costs. For U.S. manufacturers, the tariffs presented an opportunity to compete with cheaper imports, but they also faced higher prices for raw materials, many of which are sourced internationally.
The complex global supply chains in the textile industry meant the tariffs caused disruptions at multiple levels. Retailers in the U.S. were forced to pass increased costs onto consumers, while smaller businesses struggled to adapt to the changing trade policies. Additionally, the uncertainty surrounding trade relations created challenges for long-term planning and investment within the textile sector.
While the tariffs aimed to boost domestic production, the overall impact on the U.S. textile industry remained a topic of debate. Some manufacturers benefited from reduced competition, while others suffered due to higher costs and limited access to global markets. The long-term effects of these policies highlight the delicate balance between protecting domestic industries and maintaining global trade relationships.

Subscribe
- Never miss a story with notifications
- Browse free from up to 5 devices at once
- Gain full access to our premium content
Media Packs
Expand Your Reach With Our Customized Solutions Empowering Your Campaigns To Maximize Your Reach & Drive Real Results!
– Access The Media Pack Now!
– Book a Conference Call
– Leave Message for us to Get Back
Related stories
Latest stories
Related stories
Subscribe
- Never miss a story with notifications
- Gain full access to our premium content
- Browse free from up to 5 devices at once
Media Packs
Expand Your Reach With Our Customized Solutions Empowering Your Campaigns To Maximize Your Reach & Drive Real Results!
– Access The Media Pack Now!
– Book a Conference Call
– Leave Message
for us to Get Back