The Impact of Reciprocal Tariffs on U.S. Manufacturing in the Textile and Apparel Industry
In recent years, the discussion surrounding the revival of US textile manufacturing has gained momentum, particularly in the textile and apparel sectors. The implementation of reciprocal tariffs under President Donald Trump’s administration has sparked a complex debate over the potential for reshoring manufacturing back to the United States, challenging the dominance of traditional manufacturing hubs such as China and other Asian countries. This article delves into the implications of these tariffs, the prospects for the revival of US textile manufacturing, and the challenges that lie ahead for the textile and apparel industry.
Understanding Reciprocal Tariffs
Reciprocal tariffs are designed to impose equivalent duties on imports from countries that impose tariffs on U.S. exports. Trump’s administration positioned these tariffs as a strategy to protect American workers and industries from unfair foreign competition, particularly targeting nations accused of manipulating their currencies or engaging in predatory trade practices. The goals were twofold: to level the playing field for U.S. manufacturers and to encourage domestic production by making imports less competitive.
The Textile and Apparel Sector
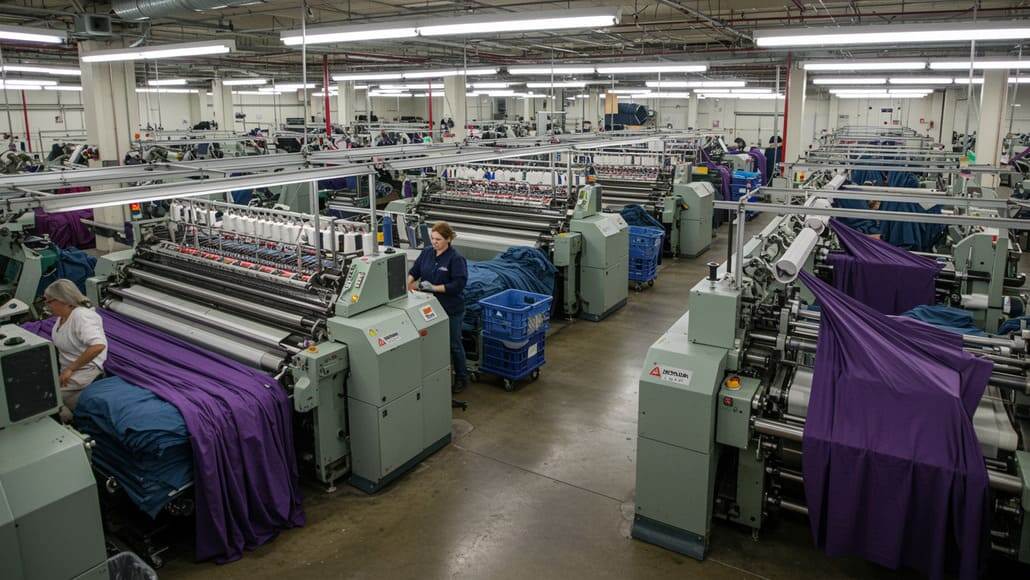
Historically, the textile and apparel industry has been a significant component of the U.S. manufacturing landscape. However, over the past few decades, much of this production has shifted to countries with lower labor costs, primarily in Asia. The U.S. once boasted a robust textile industry, but it has faced a stark decline due to globalization and offshoring practices.
According to the National Council of Textile Organizations (NCTO), the U.S. textile industry employs approximately 600,000 workers, significantly down from its peak in the 1990s. The implementation of reciprocal tariffs aims to curtail reliance on imports and revitalize this vital sector. Achieving the revival of US textile manufacturing is essential for restoring jobs and enhancing economic stability.
Potential for Reshoring Manufacturing
The prospect of reshoring manufacturing to the U.S. has raised hopes among industry stakeholders. Proponents argue that the combination of reciprocal tariffs and a renewed focus on domestic production could restore jobs and create new opportunities in the textile and apparel sectors. Tariffs on imports from countries like China could make domestically produced textiles more competitive, potentially encouraging brands to invest in U.S. manufacturing capabilities.
A survey conducted by the American Apparel and Footwear Association (AAFA) indicated that while many companies envision a return to domestic production, they also emphasize the need for strategic planning and investment in modern manufacturing technologies to remain competitive. The integration of automation and sustainable practices could play a pivotal role in improving productivity and reducing costs, thus facilitating the revival of US textile manufacturing.
Challenges Faced by U.S. Manufacturers
Despite the potential for a manufacturing renaissance, significant challenges exist. One of the most pressing issues is the current gap in skilled labor. The U.S. textile industry has struggled to attract and retain a workforce capable of meeting modern manufacturing demands. Many skilled workers have either retired or transitioned to other industries, resulting in a talent shortage that hampers production capabilities.
Moreover, while reciprocal tariffs may deter imports from countries like China, they can also lead to retaliatory measures, escalating trade tensions and complicating relationships with key trading partners. For instance, the textile industry has expressed concerns that higher tariffs on apparel and textiles could disproportionately affect lower-income consumers, leading to increased prices for everyday clothing and undermining consumer confidence. Addressing these challenges will be critical to ensuring the success of the revival of US textile manufacturing.
Competing with China and Other Asian Manufacturers
China remains a formidable competitor in the textile and apparel manufacturing landscape. With its vast production infrastructure, established supply chains, and economies of scale, China can produce textiles at lower costs than many Western competitors. The American textile industry faces an uphill battle if it seeks to compete solely on price.
To successfully challenge China and other Asian manufacturers, U.S. textile companies must leverage their strengths, focusing on quality, innovation, and sustainability. Brands are increasingly emphasizing ethical production practices, and U.S. manufacturers can appeal to consumers who prioritize sustainability and responsible sourcing. By investing in advanced manufacturing technologies and sustainable practices, U.S. companies can differentiate themselves from lower-cost competitors, advancing the goal of the revival of US textile manufacturing.
The Role of Technology in Revitalization
To tackle the challenges posed by globalization and competition from Asian manufacturers, the U.S. textile industry must embrace technological advancements. Automation and digitization can lead to increased efficiency and reduced production costs, allowing companies to compete more effectively. Additionally, the integration of data analytics and supply chain management tools can enhance decision-making processes and optimize operations.
Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic underscored the importance of resilient supply chains. Companies that diversify their sourcing strategies and implement agile manufacturing processes will be better positioned to navigate future disruptions, whether due to geopolitical tensions or global health crises. These advancements are vital for promoting the revival of US textile manufacturing and ensuring its long-term competitiveness.
Conclusion
The implementation of reciprocal tariffs under the Trump administration has opened a dialogue around the revival of US textile manufacturing in the textile and apparel industry. While these tariffs present an opportunity to encourage reshoring, they also introduce challenges that require careful navigation. The U.S. must address the skills gap, invest in technological advancements, and find innovative ways to compete with established manufacturing giants like China.
As stakeholders explore the potential for revitalization, collaboration between industry players, policymakers, and educational institutions will be crucial. By fostering a culture of innovation, prioritizing sustainability, and supporting workforce development, the U.S. textile industry can position itself for success in a rapidly evolving global landscape. The path ahead may be fraught with challenges, but with strategic efforts, a resurgence of manufacturing in the U.S. is within reach, ultimately achieving the revival of US textile manufacturing.