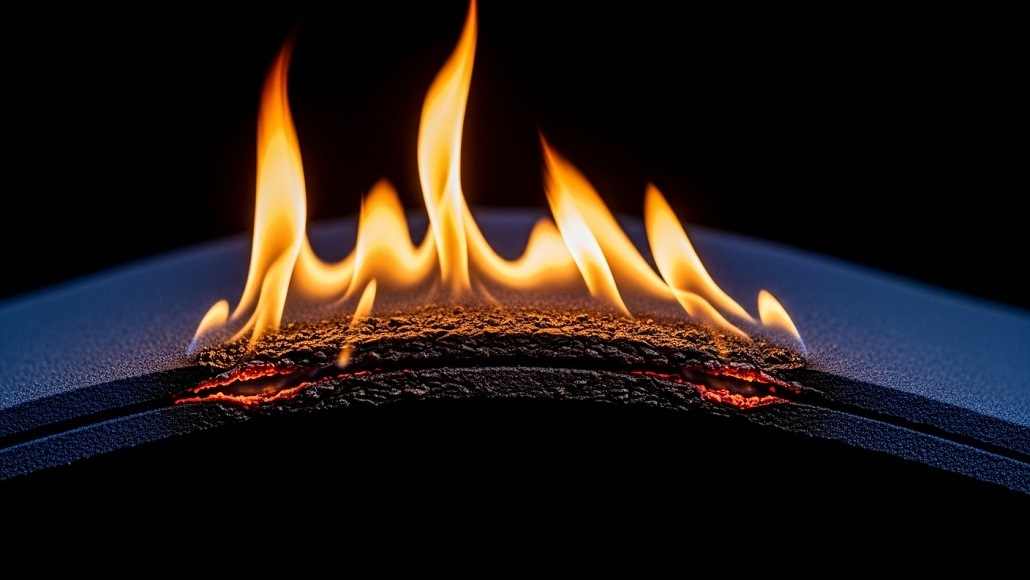
Flame-retardant fabrics have quietly become a backbone of safety across industries—from military and firefighting gear to furniture and public transport. As demand surges for safer, sustainable, and high-performance textiles, this article unpacks the production science, global market evolution, and future potential of flame-resistant materials redefining modern protection.
Flame-Retardant Fabrics: The Safety Revolution
When we think of clothing or upholstery, we rarely consider how it might react in a fire. Yet, for millions of people—firefighters, military personnel, industrial workers, and even airline passengers—fabric performance under extreme heat can mean the difference between life and death. Enter flame-retardant fabrics: engineered textiles that resist ignition, limit flame spread, and offer critical seconds of protection in dangerous situations.
In a world where risk is unavoidable, flame-retardant fabrics are helping create a safer future, thread by thread.
A Silent Guardian in Our Surroundings
These textiles are present in more places than one might expect. From airplane seats to children’s pajamas, from electrical cable jackets to the coats of oil rig workers, flame-retardant materials are integral yet often invisible. They shield without shouting. Their unassuming role belies their importance.
As Elon Musk once remarked:
“Some people don’t like change, but you need to embrace change if the alternative is disaster.”
Flame-retardant technology embodies that ethos—preventing disaster before it starts.
How Flame-Retardant Fabrics Work
At the molecular level, flame-retardant fabrics resist combustion by altering the way materials behave when exposed to high temperatures. This resistance can be achieved either by modifying the raw fibers themselves (inherent flame resistance) or by treating finished fabrics with chemical additives (treated flame retardants).
Inherent flame-resistant fibers—like aramids (e.g., Nomex, Kevlar), modacrylics, and carbon blends—have heat resistance baked into their structure. They don’t melt, drip, or support combustion. These are often used in garments for firefighters and pilots.
Treated fabrics, such as cotton or polyester infused with flame-retardant chemicals, offer flexibility and cost-effectiveness for industries like furniture or home textiles. These treatments form insulating char layers or release gases that dilute oxygen around the fabric, slowing the burning process.
The type of fabric, the finishing process, and the end-use application all shape how flame-retardant properties are engineered.
Industrial Applications: From Fire Gear to Furnishings
Flame-retardant fabrics are crucial in sectors where heat, sparks, or chemical exposure are routine. In firefighting and emergency services, turnout gear made from aramid-based fabrics withstands temperatures exceeding 1000°F. For military personnel, flame-resistant uniforms protect against flash fires and IED explosions.
In industrial settings—especially oil, gas, electrical, and welding environments—FR garments provide a first line of defense. In these high-risk arenas, the U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) mandates the use of flame-resistant clothing (FRC) under many conditions.
Beyond personal protection, flame-retardant fabrics are essential for public safety. Seats in buses, planes, and trains are mandated by regulation to meet flammability standards. Curtains, carpets, tents, and wall linings in public buildings must comply with fire safety codes using such fabrics.
Production and Technology: Chemistry Meets Engineering
Producing flame-retardant fabrics involves two main approaches: fiber innovation and chemical finishing.
In the case of inherent FR fabrics, the fiber composition is modified during polymerization. Aramid fibers, for instance, are spun from aromatic polyamides which resist heat and are non-conductive. These fibers are then woven or knitted into fabric structures optimized for durability, comfort, and breathability.
Treated fabrics, on the other hand, undergo specialized finishing processes post-production. This may involve pad-dry-cure techniques where chemicals are embedded and cured into the fiber matrix, or plasma treatments and sol-gel coatings for eco-friendlier results.
The challenge lies in maintaining the balance between fire resistance and fabric comfort, particularly for daily-wear garments. This is where nanotechnology and bio-based retardants are pushing the boundaries. Scientists are now exploring biodegradable and halogen-free compounds derived from phosphorus, nitrogen, and even plant oils to create greener, safer finishes.
As Dr. Bryan Haynes of Kimberly-Clark noted in a materials science summit:
“The next frontier is flame retardancy without compromise—on health, sustainability, or performance.”
Global Market Outlook: Growth Ignited by Safety Awareness
According to a 2024 report by MarketsandMarkets, the global flame-retardant textile market is projected to grow from USD 4.8 billion in 2023 to USD 7.9 billion by 2030, registering a CAGR of over 7.5%. This growth is fueled by:
-
Tighter safety regulations in construction, aviation, and industrial sectors
-
Rising defense budgets across NATO and Asia-Pacific countries
-
Demand for high-performance workwear in developing economies
-
Increasing consumer awareness of fire safety in residential textiles
North America currently leads the market due to stringent fire codes and industrial safety mandates. Europe follows closely with strong standards for eco-friendly flame retardants. Meanwhile, Asia-Pacific is poised to experience the fastest growth, thanks to rapid urbanization, infrastructure development, and domestic manufacturing incentives in China, India, and Southeast Asia.
Challenges and Environmental Considerations
Despite the lifesaving benefits, flame-retardant fabrics face scrutiny for their environmental and health impacts. Some older halogenated chemicals used in fabric treatments have been linked to toxicity, bioaccumulation, and endocrine disruption.
In response, regulators like the EU’s REACH and California’s Proposition 65 have restricted or banned many of these substances. This has triggered a wave of innovation in alternative chemistries and bio-based materials.
Eco-certifications such as OEKO-TEX, GOTS, and Bluesign are increasingly required by global buyers to ensure flame-retardant textiles are not only safe in use but also sustainable in production.
Industry leaders are investing heavily in clean technologies. Companies like Teijin, Milliken, DuPont, and TenCate are leading the charge in sustainable FR development—seeking durable, recyclable, and non-toxic solutions that maintain performance in real-world settings.
The Future Fabric of Protection
The evolution of flame-retardant fabrics is far from over. As industries grow more complex and climate risks intensify, the demand for multi-functional, lightweight, and breathable fire-resistant textiles is expected to skyrocket.
Emerging trends include:
-
Smart FR fabrics that change color or alert wearers upon exposure to heat
-
Energy-absorbing fabrics with integrated thermal sensors
-
Modular FR uniforms designed for extreme weather and agile deployment
-
Fully circular FR garments built for reuse, recycling, and remanufacturing
“True safety,” as astronaut Chris Hadfield once said, “comes from not only preparing for the worst—but designing so it’s unlikely to occur.”
Flame-retardant fabrics embody that ethos. They are not just reactive protection but proactive design—preventing harm before it starts. From battlefields to bedrooms, these high-performance textiles are sewing safety into every seam of modern life.
Conclusion: More Than a Protective Layer
Flame-retardant fabrics are no longer niche solutions but foundational components of safety, resilience, and compliance across sectors. Their production involves sophisticated science, engineering ingenuity, and a growing dose of sustainability.
As regulations tighten and performance expectations rise, the fabric of safety must evolve accordingly. In that evolution lies not just technological progress, but a quiet revolution in how we protect lives—with the very materials we wear, sit on, or sleep under.
When safety meets science, and function meets fabric, we get more than clothing. We get confidence.