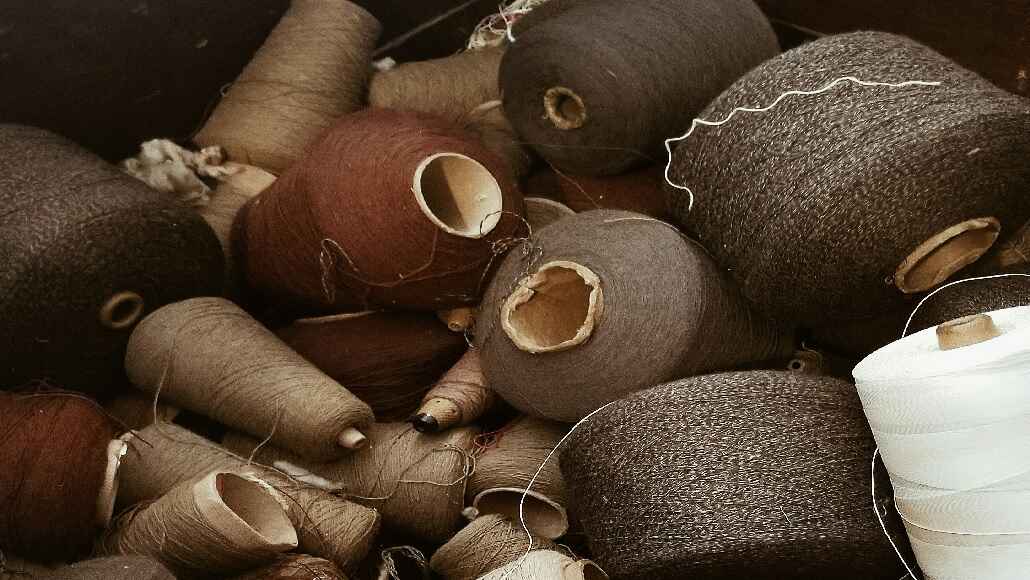
The closure of three key land ports between Bangladesh and India has disrupted India-Bangladesh yarn exports, pushing Indian textile mills to explore alternative transportation options. These land ports previously facilitated nearly 30% of India’s yarn exports, making their closure a significant challenge for the industry.
Indian textile exporters have called on the government to engage in discussions with Bangladesh to resolve the issue. During a recent meeting, exporters evaluated various alternatives, including container shipping and inland waterways, while also holding meetings with Bangladeshi buyers to find workable solutions.
“The problem in sending the goods in containers by sea is the lead time. Even now, 70% of the Indian yarn to Bangladesh goes by sea. Those who exported through land ports will also use the sea now. There are smaller ships that go from Kolkata. The possibility of sending in those ships needs to be explored,” said Siddhartha Rajagopal, executive director of the Cotton Textiles Export Promotion Council.
Impact on Yarn Exports and Domestic Market
K. Selvaraju, secretary general of the Southern India Mills’ Association, emphasized the importance of India-Bangladesh yarn exports, which constitute nearly 45% of India’s total yarn exports. While India used to export over 100 million kilograms of yarn monthly, the figure has fallen to around 90 million kilograms. With China reducing its imports of Indian yarn in recent years, Bangladesh remains a critical market.
“If the 30% exports to Bangladesh are affected, the yarn will shift to domestic consumption, driving down prices and disrupting the domestic textile value chain,” Selvaraju stated.
Broader Industry Concerns
The closure of land ports has already started to impact textile mills, particularly in northern states. Selvaraju warned that if the situation is not resolved, it could have far-reaching consequences, potentially affecting the entire textile spinning sector across India.
As the industry contends with these challenges, finding efficient alternative routes and solutions remains crucial to stabilizing India’s textile sector and sustaining its export relationship with Bangladesh.