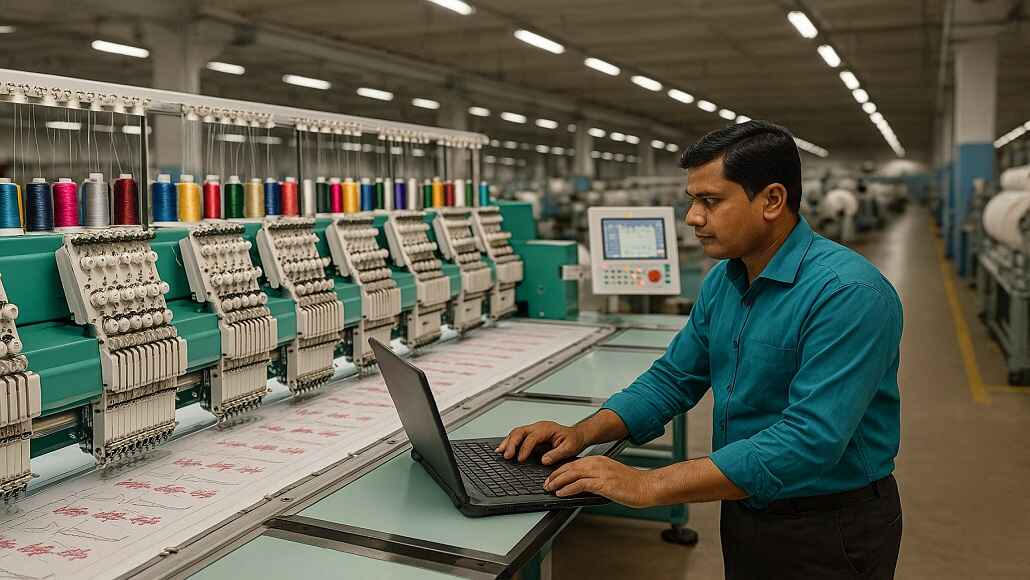
In a significant shift aimed at maintaining its status as the world’s second-largest garment exporter, Bangladesh is ramping up its efforts to modernize its textile industry by focusing on strong technology transfers and upgrading machinery. With changing global buyer expectations leaning towards sustainability, automation, and traceability, industry leaders and policymakers in Bangladesh are welcoming innovations to enhance competitiveness, elevate quality, and minimize environmental impact.
A Transformative Era: Technology Adoption in Bangladesh’s Textile Industry
Technology adoption—understood as the integration of new machinery, software, and best practices from leading global markets—is recognized as a crucial element for rejuvenating Bangladesh’s textile value chain. Innovations such as automated spinning machines, environmentally friendly dyeing processes, AI-driven inventory systems, and blockchain-enabled traceability platforms are reshaping production processes across spinning, weaving, dyeing, and finishing sectors.
“Technology is key to future textile competitiveness,” asserted industry specialists during recent discussions. “Bangladesh cannot solely depend on low-cost labor anymore. Innovation has to be our foundation.”
While major players like Beximco, Square Textiles, DBL Group, and Envoy Textiles have made significant investments, smaller factories still encounter difficulties in upgrading from traditional equipment. This inconsistency presents challenges in ensuring uniform quality, efficiency, and sustainability throughout the industry.
The Importance of Timely Transformation
The need for transformation is becoming increasingly urgent as Bangladesh’s primary competitors—Vietnam, China, and India—amplify investments in smart manufacturing and sustainable textiles. The advantages of technology transfer for Bangladesh include:
-
Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Achieved through automation and AI integration
-
Upgraded Product Quality: Ensuring consistency
-
Environmental Compliance: Meeting international standards
-
Design Flexibility: Made possible by digital tools like CAD/CAM
-
Reduced Lead Times: Enabling quick responses to rapidly evolving global fashion trends
Nevertheless, progress is hindered by several obstacles, including high capital requirements, a shortage of skilled labor, outdated infrastructure, and weak research and development connections between industry and educational institutions.
Strategic Framework: Advancing Technology Adoption
To promote the widespread adoption of technological innovations across the sector, Bangladesh is concentrating on:
-
Textile Technology Parks: Featuring shared R&D facilities, plug-and-play infrastructure, and training centers
-
Incentive Schemes: Including tax incentives and expedited import processes for smart and green technology
-
Skill Development Programs: Offered through institutions like NITER and BGMEA University of Fashion & Technology
-
Collaborations Between Universities and Industry: Fostering localized innovation and process enhancements
-
Global Alliances: Partnering with organizations like ITMA, GIZ, and JICA
Initiatives such as the Green Transformation Fund (GTF) and the Export Competitiveness Program are already yielding positive outcomes, assisting in the purchase of green machinery and pilot projects for digital transformation.
Modernizing Textile Machinery: A Pathway to Sustained Growth
Central to this transformation is Bangladesh’s ambition to revamp its textile machinery sector. From energy-efficient spinning lines and digital printing technology to advanced finishing systems, leading manufacturers are heavily investing in state-of-the-art equipment from renowned global OEMs like Trützschler, Picanol, Saurer, and Toyota.
The Bangladesh Textile Mills Association (BTMA) reports that over $5 billion has been allocated to new machinery in the past five years. These advancements are facilitating:
-
Higher speed and capacity with reduced human error
-
Adherence to global environmental, social, and governance (ESG) standards
-
Decreased waste and lower resource consumption
-
Enhanced design accuracy and product innovation
Government-supported initiatives like the Technology Upgradation Fund play a crucial role in assisting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) in closing the investment gaps. Meanwhile, international financing options such as the GTF are bolstering the acquisition of low-impact, energy-efficient machinery.
Ongoing Challenges
Despite the positive trajectory, several challenges continue to impede progress:
-
Financial hurdles for small to medium-sized mills
-
Limited availability of skilled technicians
-
Inconsistent after-sales service and spare parts supply
-
Policy deficiencies in streamlining approval and customs processes for imported technology
Experts underline the necessity of a collaborative industry-wide approach: integrating financial incentives, policy reforms, skills training, and global cooperation.
Looking Ahead
As Bangladesh aims for $100 billion in apparel exports by 2030, adopting smart and sustainable technologies has become essential. The modernization of textile machinery and effective technology transfer will shape the next phase of Bangladesh’s industrial development. With a forward-thinking strategy, strengthened public-private partnerships, and global innovation collaborations, the nation is well-positioned to evolve from a low-cost manufacturing center to a value-added, innovation-centric textile powerhouse.